Trauma affects millions of people worldwide, yet many mental health professionals lack specialized training to address these complex conditions effectively.
We at Devine Interventions understand that proper trauma therapy course education transforms both practitioners and their clients’ lives. This comprehensive guide examines evidence-based approaches and the significant benefits of professional trauma therapy training.
Understanding Trauma and Its Impact
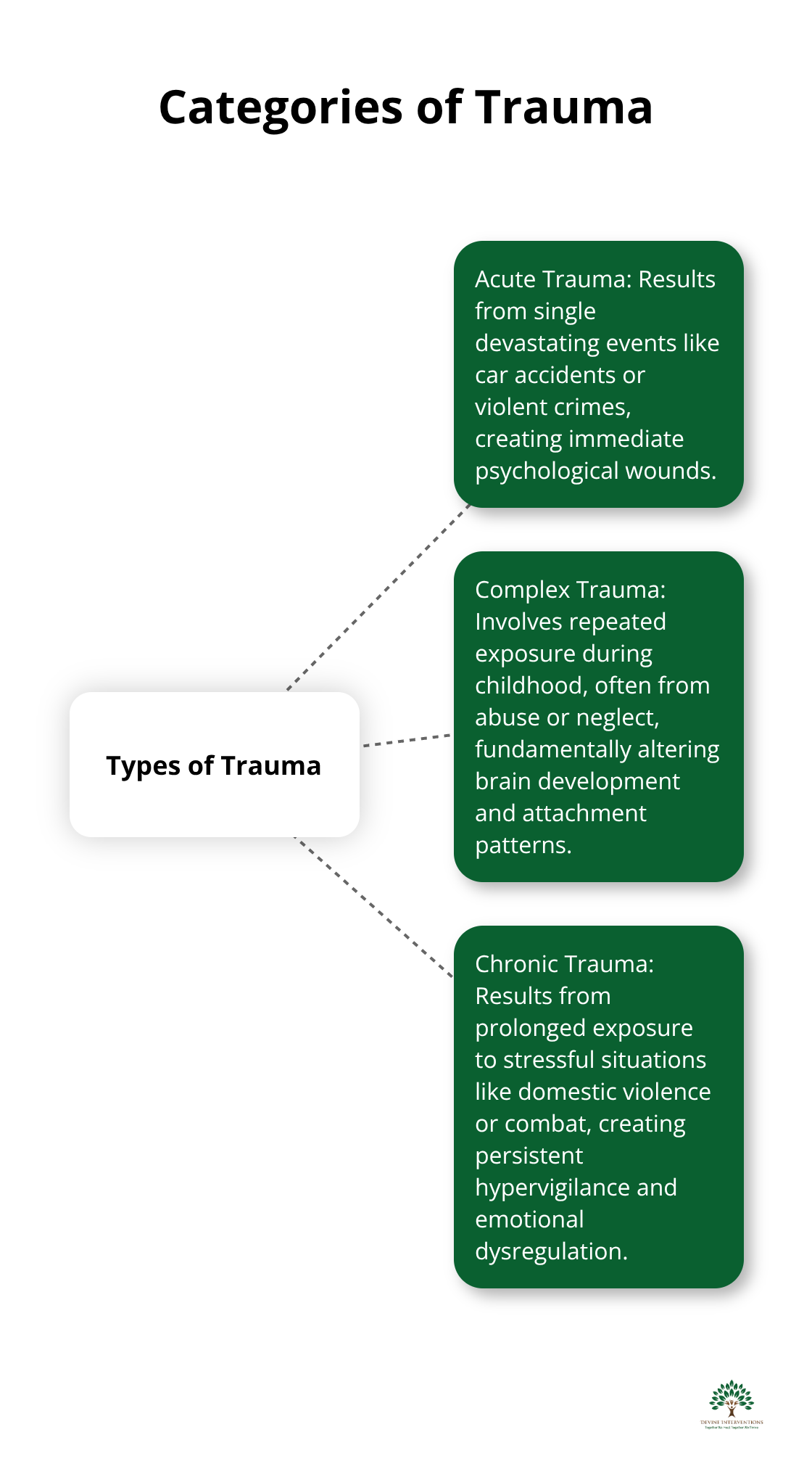
The Three Categories That Define Trauma
Acute trauma strikes from single devastating events like car accidents or violent crimes, affecting many adults who experience various forms of traumatic incidents. These incidents create immediate psychological wounds that develop into lasting mental health conditions without proper treatment. Complex trauma involves repeated exposure during childhood, often from abuse or neglect, and fundamentally alters brain development and attachment patterns. Chronic trauma results from prolonged exposure to stressful situations like domestic violence or combat, creating persistent hypervigilance and emotional dysregulation that affects every aspect of daily life.
How Trauma Rewires Your Brain and Body
Trauma physically changes brain structure, particularly in areas that control memory, emotion regulation, and stress response. The amygdala becomes hyperactive while the prefrontal cortex (responsible for rational thought) becomes impaired. This neurobiological damage explains why trauma survivors experience flashbacks, panic attacks, and difficulty with concentration. The body stores trauma through chronic muscle tension, digestive issues, and compromised immune function. These represent measurable physical changes rather than psychological weaknesses, and they require specialized therapeutic intervention to heal properly.
Warning Signs Mental Health Professionals Must Recognize
Trauma manifests through specific behavioral patterns that untrained professionals often misinterpret. Clients may exhibit sudden mood swings, dissociation during sessions, or extreme reactions to seemingly minor triggers. Physical symptoms include chronic headaches, insomnia, and unexplained pain. Social withdrawal, substance abuse, and self-destructive behaviors frequently emerge as coping mechanisms. Depression and anxiety disorders commonly co-occur with trauma, creating complex treatment challenges that demand specialized approaches.
These complex presentations highlight why traditional talk therapy methods often fall short when trauma underlies mental health conditions. Mental health professionals need evidence-based trauma therapy approaches to address these multifaceted symptoms effectively.
Evidence-Based Trauma Therapy Approaches
Trauma-Focused CBT Delivers Rapid Results
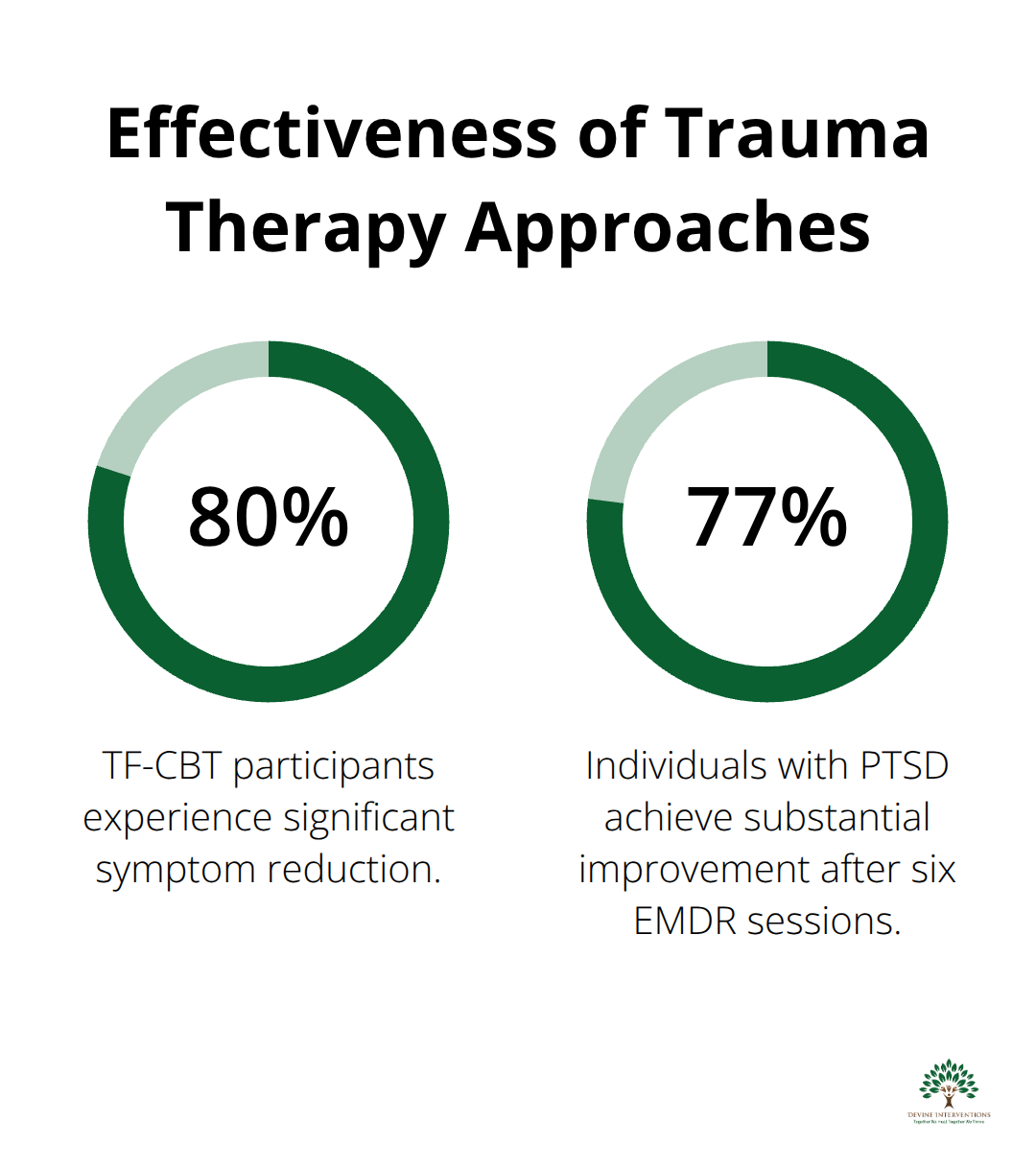
Trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy produces measurable improvements within 12-16 sessions for most clients. This approach targets the distorted thought patterns that maintain trauma symptoms and teaches clients to identify triggers while they reframe catastrophic thoughts. The American Psychological Association rates TF-CBT as a first-line treatment because studies show 80% of participants experience significant symptom reduction. Therapists apply specific techniques like cognitive processing therapy and prolonged exposure, which systematically address avoidance behaviors that prevent recovery. TF-CBT works particularly well for single-incident trauma and helps clients develop concrete coping strategies they can use immediately when symptoms surface.
EMDR Processes Memories Without Verbal Recounting
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing processes traumatic memories without requiring detailed verbal descriptions, which makes it ideal for clients who struggle with traditional talk therapy. Research published in the Journal of Clinical Psychology found that EMDR therapy helped 77% of individuals with PTSD achieve substantial improvement after just six sessions. This method helps clients process stuck memories while they remain grounded in the present moment. EMDR works by activating the brain’s natural healing processes through bilateral stimulation (typically eye movements), which allows traumatic memories to integrate properly into long-term memory storage.
Somatic Therapies Address Physical Trauma Storage
Somatic therapies like trauma-sensitive yoga and body awareness techniques address the physical manifestations of trauma that cognitive approaches often miss. These methods help clients reconnect with their bodies safely and release chronic tension patterns that develop after traumatic experiences. Practitioners guide clients through gentle movement and breathing exercises that restore the nervous system’s natural regulation. The body stores trauma through muscle memory and nervous system dysregulation, so these approaches target healing at the physiological level where traditional talk therapy cannot reach.
Group and Family Therapy Rebuild Connection
Group therapy formats provide peer validation and reduce isolation, with studies showing participants in trauma-focused groups maintain treatment gains longer than those in individual therapy alone. Family therapy becomes essential when trauma affects relationship dynamics, particularly for childhood trauma survivors who need to rebuild trust and communication patterns with loved ones. These collaborative approaches address the relational wounds that trauma creates and help clients develop healthy support systems. Professional trauma therapy training equips mental health practitioners with these specialized skills that transform treatment outcomes.
Benefits of Professional Trauma Therapy Training
Advanced Skills Transform Clinical Practice
Mental health professionals who complete specialized trauma therapy training develop enhanced clinical capabilities through comprehensive educational programs. These programs teach specific techniques like bilateral stimulation protocols for EMDR, somatic regulation exercises, and trauma-focused CBT interventions that general therapy education never covers. Trained professionals learn to recognize subtle dissociation signs, implement grounding techniques during sessions, and safely navigate trauma memories without retraumatizing clients. The National Child Traumatic Stress Network found that therapists with trauma certification demonstrate measurably better clinical judgment when they work with survivors of childhood abuse, domestic violence, and combat trauma.
Client Outcomes Improve Dramatically
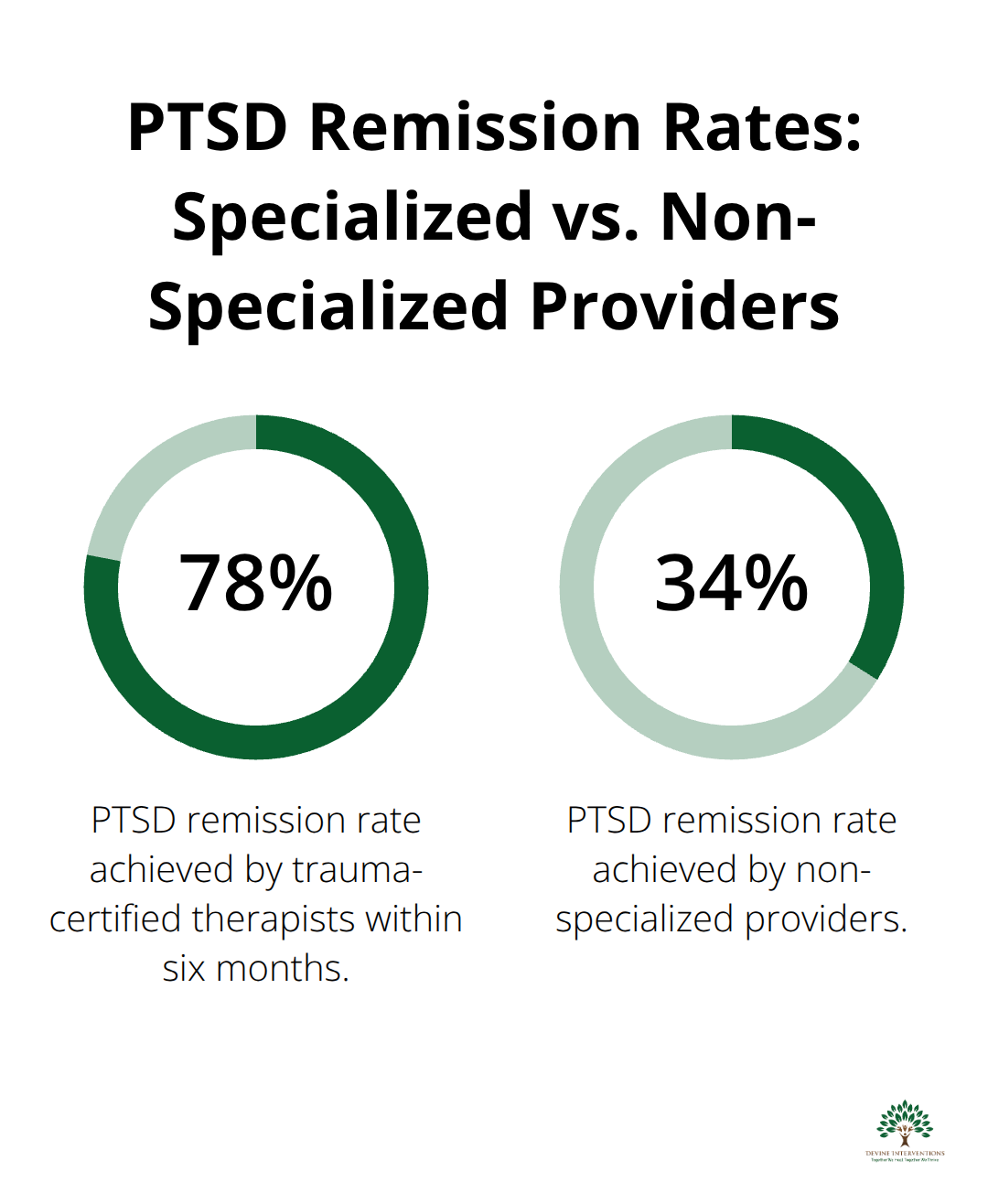
Clients treated by trauma-trained therapists show improved outcomes through specialized intervention approaches. Treatment dropout rates decrease from 40% to 15% when therapists possess trauma-specific credentials. Specialized training teaches professionals how to pace therapy appropriately, prevent client overwhelm, and maintain therapeutic relationships even when clients exhibit challenging behaviors like anger outbursts or emotional shutdown. The Veterans Administration reports that trauma-certified therapists achieve PTSD remission rates of 78% within six months, compared to 34% for non-specialized providers.
Career Advancement Accelerates Rapidly
Career advancement opportunities multiply rapidly for trauma-trained professionals, with specialized positions offering salary increases of $15,000-25,000 annually. These professionals receive priority consideration for supervisory roles, private practice referrals, and consultation contracts with hospitals and community organizations. Trauma specialists often develop expertise in specific populations (veterans, children, or sexual assault survivors) which creates niche markets with higher compensation rates. Many trauma-trained therapists transition into training roles themselves, teaching other professionals and establishing themselves as recognized experts in their field.
Final Thoughts
Specialized trauma treatment represents the difference between surface-level symptom management and genuine recovery. Mental health professionals who complete a comprehensive trauma therapy course develop the advanced skills needed to address complex trauma presentations that traditional approaches cannot reach. These specialized interventions produce measurably better outcomes, with trained therapists achieving PTSD remission rates nearly double those of non-specialized providers.
The transformation extends beyond individual sessions to create safer therapeutic environments. Trauma-informed professionals reduce treatment dropout rates and help clients rebuild their lives from the ground up. This specialized knowledge becomes particularly valuable when professionals work with survivors of childhood abuse, combat trauma, or domestic violence who require nuanced understanding of their unique needs.
We at Devine Interventions combine evidence-based trauma therapies with compassionate case management (serving children, adolescents, and adults across all treatment levels). Through individual therapy, group sessions, and specialized programs, we address the root causes of trauma-related conditions while we build lasting support systems. The path to recovery begins when you connect with trauma-informed professionals who understand the complexity of your experience and possess the specialized skills to guide your recovery journey effectively.







