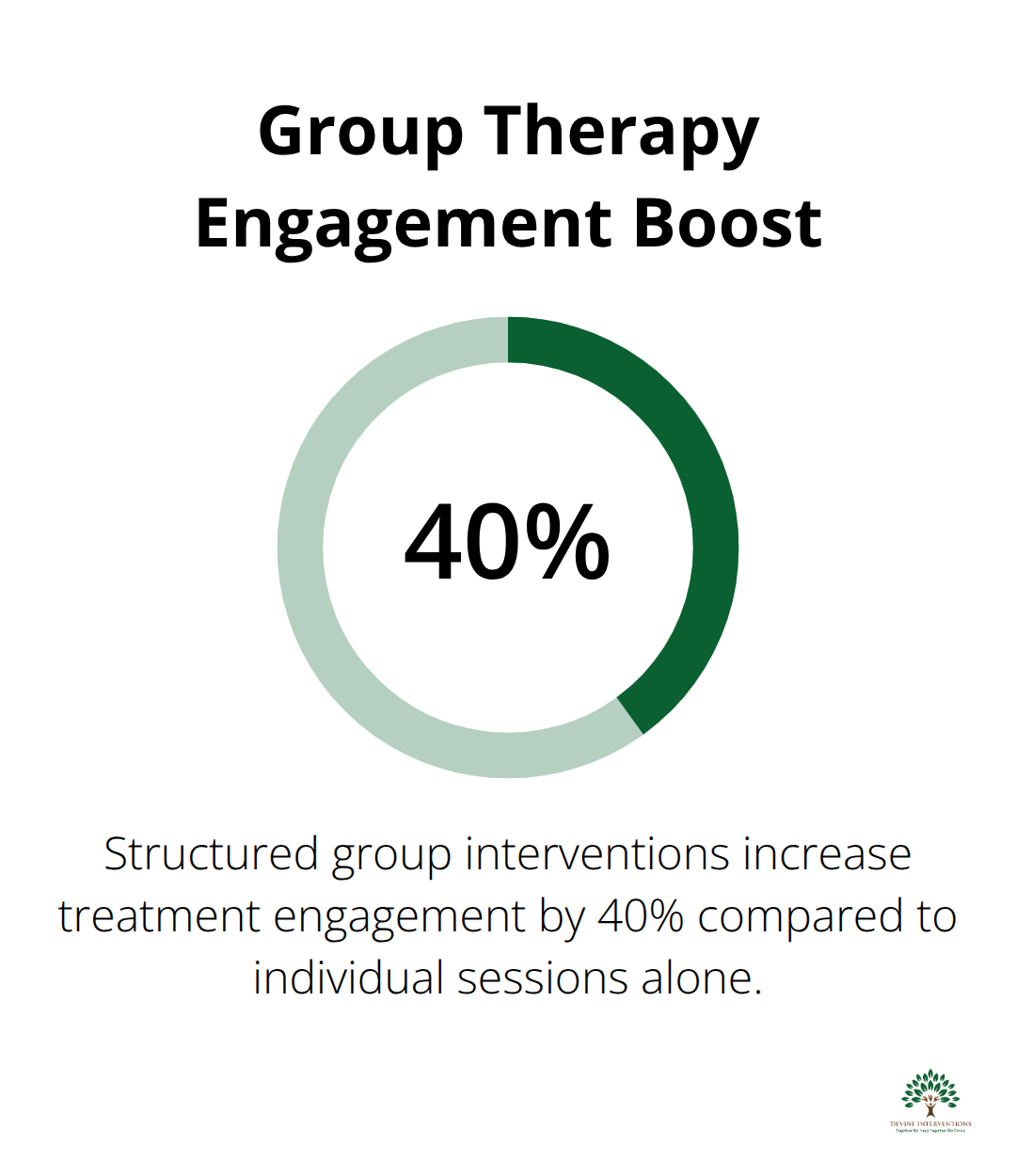
Group therapy activities can transform healing journeys when planned thoughtfully. Research shows that structured group interventions increase treatment engagement by 40% compared to individual sessions alone.
We at Devine Interventions understand that effective activity planning requires balancing therapeutic goals with participant needs. This guide provides 150 more group therapy activities and tips to help you create meaningful, evidence-based sessions that foster connection and growth.
What Makes Group Therapy Activities Work
Successful group therapy activities begin with clear therapeutic objectives that align with your group’s specific needs. Research shows that evidence-based group therapy treats anxiety, trauma, PTSD and addiction using proven methods like CBT and DBT in structured, peer-supported settings.
Start each session with identification of your target area: emotional regulation, social skills, or cognitive restructuring. Groups in the initial formation stage require trust-building activities like structured introductions and boundary-setting exercises. Working-stage groups benefit from deeper processing activities such as cognitive restructuring exercises or trauma-informed art therapy. Mature groups can handle complex role-playing scenarios and peer feedback sessions.
Adapting Activities to Group Development Phases
Group dynamics shift dramatically across developmental phases and demand different activity approaches. Storming-phase groups need conflict resolution exercises and communication skill-building, while norming groups respond well to collaborative problem-solving tasks. Research suggests there is great deal of continuity in relationship quality development within group settings.
Track your group’s emotional temperature and adjust accordingly. High-anxiety sessions call for mindfulness exercises and grounding techniques, while low-energy groups benefit from movement-based activities or creative expression tasks. Facilitators who adapt their approach based on real-time group assessment rather than rigid session plans see remarkable progress.
Structure Versus Flexibility Balance
Effective group activities require balanced structure with flexibility for optimal engagement. Create activity frameworks that accommodate different learning styles and comfort levels simultaneously. Introverted members thrive with written reflection components before verbal sharing, while extroverted participants need immediate discussion opportunities.
Build choice points into every activity where members can select their level of participation without compromising the therapeutic process. This approach increases participation rates significantly in intensive outpatient programs and partial hospitalization settings.
The foundation you establish through thoughtful activity selection directly impacts how participants engage with specific therapeutic techniques and interventions. Group therapy sessions provide invaluable peer support that enhances the effectiveness of structured activities while fostering mental well-being through shared experiences.
Evidence-Based Activity Types and Their Applications
Cognitive-behavioral activities form the backbone of effective group therapy because they target specific thought patterns and behaviors with measurable outcomes. Thought records help participants identify negative automatic thoughts and challenge them with evidence-based alternatives. These structured approaches provide concrete tools that participants can apply immediately in their daily lives.
Activity schedules combat depression by helping members plan pleasant activities and track mood changes throughout the week. Behavioral experiments allow participants to test feared situations in graduated steps, particularly effective for social anxiety disorders. These evidence-based methods offer participants practical strategies they can implement between sessions.
Creative Expression Methods That Access Deep Emotions
Art therapy and movement exercises access emotions that verbal processing cannot reach, making them particularly valuable for trauma survivors and adolescents. Collaborative mural projects allow group members to express feelings without direct verbal disclosure while they build connection through shared creation.
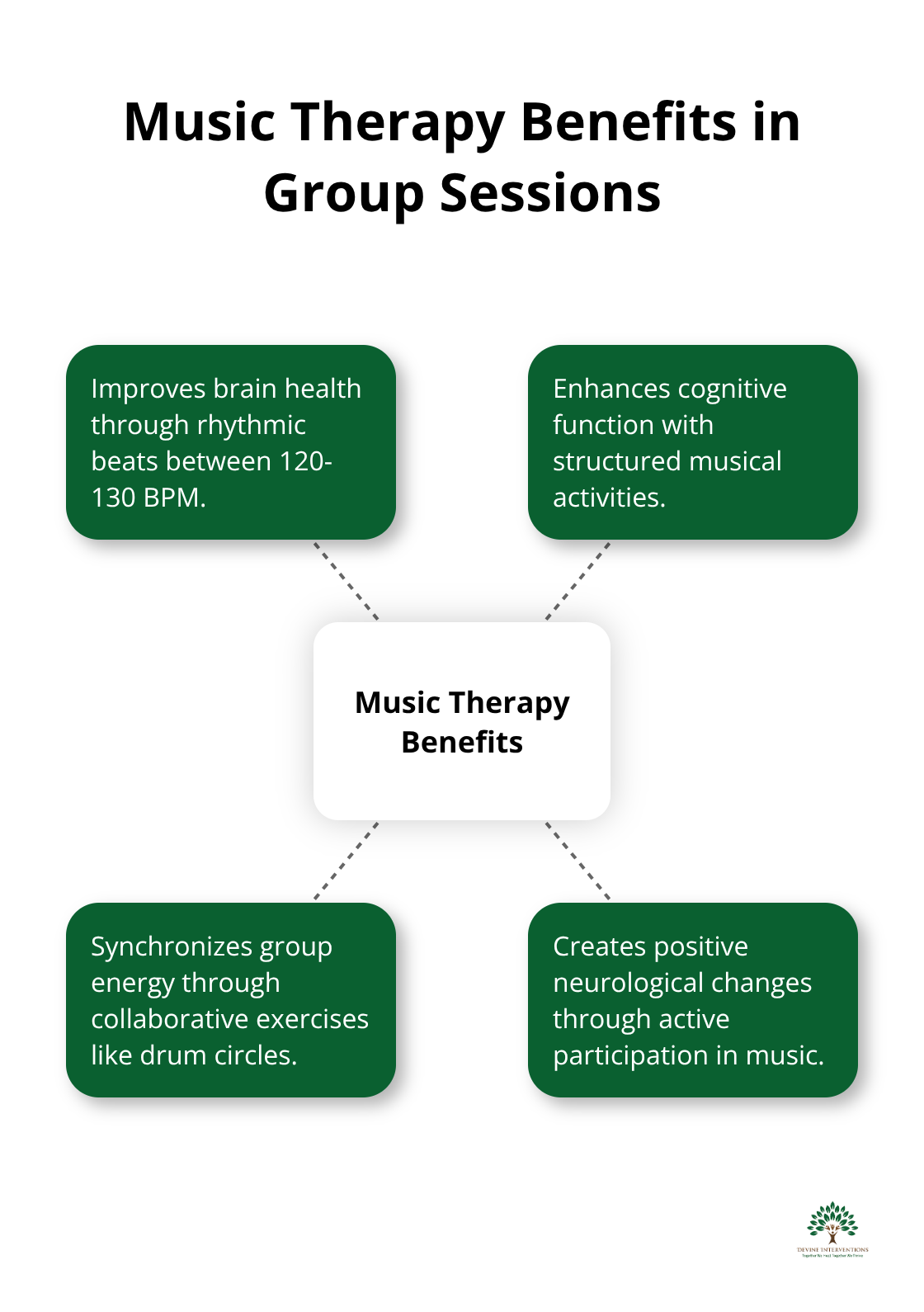
Music therapy activities like drum circles synchronize group energy and create positive neurological changes. Research shows that listening to rhythmic beats between 120-130 BPM improves brain health and cognitive function. Expressive writing exercises where participants write letters to their past or future selves generate insight breakthroughs that traditional talk therapy often misses. Movement-based activities like therapeutic dance help release trauma stored in the body while they improve group cohesion through synchronized physical expression.
Social Skills Through Interactive Practice
Role-playing scenarios provide safe practice spaces for real-world challenges without real-world consequences. Communication exercises like active listening pairs and conflict resolution simulations build interpersonal effectiveness that transfers directly to relationships outside therapy. Assertiveness training through scripted practice situations helps participants set boundaries and express needs clearly.
Interactive practice sessions that incorporate multiple feedback methods show enhanced skill development compared to single-approach techniques. Peer feedback sessions where members practice giving and receiving constructive criticism develop emotional regulation while they strengthen group bonds through vulnerability and support.
Trauma-Informed Activities for Healing
Trauma-focused group activities require specialized approaches that prioritize safety and emotional regulation. Grounding techniques like the 5-4-3-2-1 sensory method help participants stay present when difficult emotions surface. Narrative therapy exercises allow survivors to rewrite their stories from a position of strength rather than victimhood.
Body-based trauma work through gentle yoga or progressive muscle relaxation helps participants reconnect with their physical selves in safe ways. These activities work best when facilitators maintain consistent structure and clear boundaries essential for trauma recovery.
The specific techniques you choose depend heavily on your group composition, treatment setting, and available resources for implementation.
How Do You Run Group Sessions That Actually Work
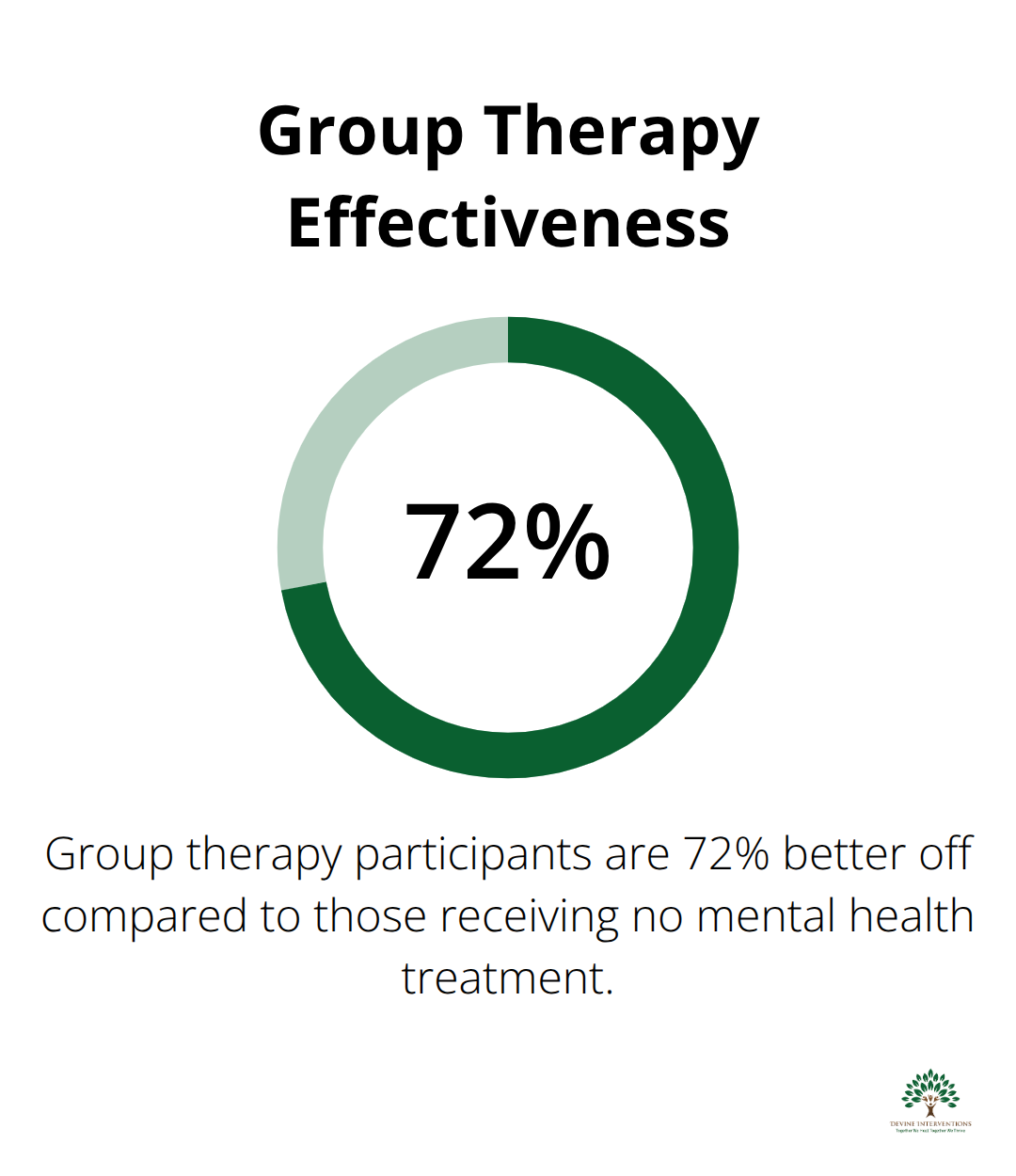
Effective group therapy sessions demand deliberate preparation and real-time adaptability that extends far beyond basic planning. Start every session with explicit ground rules that participants help establish during the first meeting. Research shows that group therapy participants are 72% better off compared to those who receive no mental health treatment, demonstrating the power of well-structured group environments.
Establish confidentiality agreements, attendance expectations, and communication guidelines that participants sign and reference regularly. Physical space setup matters tremendously: arrange chairs in circles rather than rows, maintain comfortable room temperature between 68-72 degrees, and eliminate distractions like phones or outside noise that derail therapeutic focus.
Handle Difficult Moments and Resistant Participants
Challenging behaviors emerge in every group, and your response determines whether these moments become therapeutic opportunities or session derailers. When participants dominate conversations, use the two-minute rule where each person speaks for maximum two minutes before others can respond. Silent members need direct but gentle invitations to participate through specific questions rather than general group queries.
Handle emotional outbursts by acknowledging the feeling first, then redirect energy toward group support rather than individual crisis intervention. Groups that deal with substance use disorders require different approaches than anxiety-focused groups: addiction recovery groups benefit from accountability partnerships and structured check-ins, while anxiety groups need more flexibility and emotional regulation techniques.
Adapt Activities for Different Ages and Settings
Age-appropriate modifications transform generic activities into powerful therapeutic tools that match developmental stages and treatment environments. Adolescent groups respond to technology integration like mood tracking apps and interactive games, while adult groups prefer structured discussions and practical skill-building exercises.
Intensive outpatient programs need activities that participants can practice between sessions (such as daily mood logs or communication homework assignments). Residential treatment settings allow for longer, more immersive activities like group murals or extended role-playing scenarios that outpatient groups cannot accommodate due to time constraints. High-quality drug rehab programs balance individual counseling with group therapy sessions to address both personal challenges and peer support needs.
Navigate Virtual Group Dynamics
Virtual group sessions require shorter activity segments with more frequent check-ins to maintain engagement through screen fatigue. Create breakout rooms for smaller group interactions and use screen sharing for collaborative activities. Technical difficulties will arise, so prepare backup plans and maintain flexibility when technology fails.
Final Thoughts
Successful group therapy activity plans center on three fundamental principles: clear therapeutic objectives, evidence-based interventions, and participant-centered flexibility. Track effectiveness through weekly mood assessments, participation rates, and behavioral observations rather than subjective impressions alone. Post-session feedback forms reveal which activities resonate most with your specific population.
Sustainable programs require systematic documentation of successful activities and continuous refinement based on participant outcomes. Create activity libraries that organize by therapeutic goals, developmental stages, and group sizes for easy reference. Regular supervision and peer consultation prevent facilitator burnout while they maintain program quality (essential for long-term success).
The 150 more group therapy activities and tips outlined throughout this guide provide practical frameworks that create meaningful therapeutic experiences. Implementation success depends on how well you match activities to your group’s unique needs while you maintain therapeutic boundaries and safety protocols. We at Devine Interventions support mental health professionals through evidence-based approaches. Ready to develop your group therapy skills? Contact our experienced team today to learn how we can support your professional development through proven therapeutic methods.







